
| pro | 2005/05 - 2008/02 extension and restauration of a house from the 50th, in the golden ground |
| material | exposed concrete, oak, coated steel, linoleum, zink |
| client | katja & brian jones |
| engineers | bollinger-grohmann, ffm |
‘Branding
Project Team: reinhardt_jung with Patxi Martin, Chiara Girolami, Benedetta Ercoli, Anna Vohlidalova.
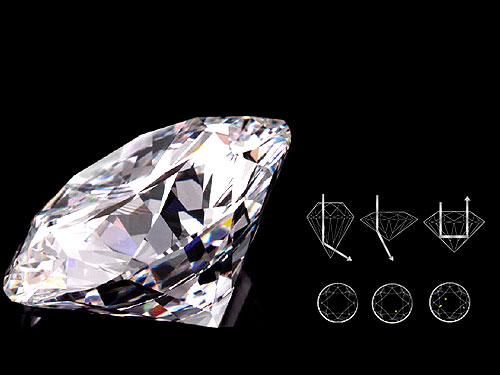
A Diamond is characterized by colour, cut, clarity and carat properties: The colour grading for white diamonds starts from completely colourless, the most expensive to a faint yellow colour. The colour in a diamond is produced from chemical impurities contained in it's composition. The whiter or colourless the diamond, the more brilliant it will be because it will allow more light to pass and be reflected back. The cut of a diamond determines shine and luminosity of a diamond, not its shape. Diamond facets allow light to internally reflect from one mirror-like facet to another and disperse. The type of diamond cut referes to reflective qualities of the diamond which determines its ability to handle light, which leads to brilliance. The clarity is a measurement of the amount of blemishes (external flaws) or inclusions (internal flaws) a diamond contains. An inclusion can air bubbles, cracks, and non-diamond minerals found in the diamond. A carat is a unit of measurement for the weight of a diamond with one carat equaling to 200 milligrams, or 0.2 grams. The price of diamonds with respect to their carat weight goes up exponentially.